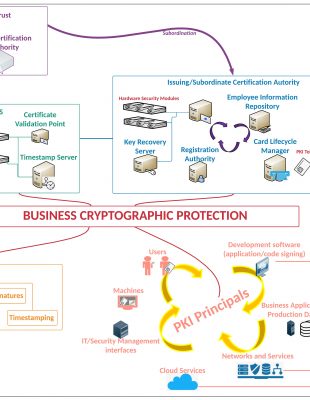
A Public Key Infrastructure is a collection of software, hardware, entities and policies that handles the entire lifecycle of digital certificates from key generation to revocation. The following stages can be identified in lifecycle of digital certificates: key generation and protection, digital certificates issuance, usage, expiration or revocation.
A Key Pair is composed of 2 strings (keys) that are connected (mathematically) but is unfeasible from math point of view to derive one from another. In the RSA algorithm (most common and used asymmetric algorithm), these keys are called RSA Public Key and RSA Private Key.
The Private Key must be heavily protected this is why recommended to have it secured on a dedicated, special-purpose device. When used at application level (Certification Authority, Web Servers, Digital Signature Servers), these devices are called Hardware Security Modules. The devices used to protect the users’ Private Keys are either Smart Cards or PKI Tokens (“smart card” embedded in a device provisioned with USB interface).
When using the RSA Public Key in performing cryptographic operation with his/her counterparts/colleagues/ partners, the user must trust presented Public Key. In order to accomplish this, a digital certificate is used.
A digital certificate is a data structure that is digitally signed by Private Key and its role is to tie the Public Key to an entity name. This trust in PKI is of type hierarchical. The Trust Point starts from the certificate of Root Certification Authority whose Private Key is used to sign digital certificates of entities choosing to participate in that specific tree. Most times, the Root Certification Authority is not used to sign the principals/end-entities directly, but an Intermediate/Issuing Certification Authority is used. This strategy to deploy the trust tree is called 2-tier PKI hierarchy.
The principals/end-entities, as users, computers/systems, applications, etc., that want to participate in the deployed PKI will validate the chain up to the Root Certification Authority so they being sure that the presented digital certificates can be trusted.
Challenges
Today’s companies have hard-times in protecting their data and keeping peace with compliance requirements. The amount of data is huge even for mid-size companies and the organization must ensure that the data is secure regardless its state, in-transit or at-rest. The data can be accessed in unauthorized way (loss of confidentiality), it can be modified inappropriately (loss of integrity), the users can be impersonated (loss of authenticity) or the systems may allow the users to deny their actions (repudiation).
Another area of concern is the management of the entire lifecycle of cryptographic keys. There should be appropriate measures to make sure that the keys are protected on each step: creation/generation, usage control, access control, expiration and change/rotation, distribution, storage, recovery, destruction/zeroization.
How can this technology help you?
A Public Key Infrastructure is not a security control by itself, but it provides cryptographic support or a large array of other controls. Practically, there is almost no security control that hasn’t a bit of cryptography and/or digital certificates, starting from hashes on malware signatures or OS/ISO images, protection of management interfaces with TLS, secure tunneling, authentication processes, etc.
Despite the other controls that take advantage of cryptography, here are some scenarios where RSA Keys can be used to enhance the protection of the critical business assets:
Digital Signatures
Ensuring Integrity, Authenticity and Non-repudiation
Document digital signing (file digital signing)
- By using desktop digital signing applications or
- By integrated Document Management services with digital signatures
Email digital signing
Bulk digital signing (for instance when you receive digitally signed bills from your service providers)
Code or Application digital signing (for instance when in application control/Mobile Device Management solutions the execution can be granted only for trusted/digitally signed software)
Encryption
Ensuring Confidentiality of the data at-rest and in-transit
SSL/TLS protection of all fundamental network services: HTTPS, LDAPS, RDPS, FTPS/sFTP (FTP over SSH), Syslog over TLS, SMTPS, IMAPS, etc.
Web Services data encryption
SSL/TLS VPN Concentrators
Email encryption
Document encryption (file encryption)
SSH tunneling (using only RSA Public/Private Keys)
Disk and folder encryption
Database encryption (using only RSA Public/Private Keys)
Authentication
Ensuring one of the factors for strong authentication
(Authentication by possession, by being in the possession of a digital certificate or a device that stores the private key)
SSL/TLS mutual authentication:
authenticating user on Web Server or by authenticating communicating peers in Web Services transactions
Smart Card Logon
(authentication of users to Active Directory by using Kerberos PKINIT)
Authentication of machines to the network
(EAPoTLS or SSL/VPN NAC)
Authentication of users in order to establish VPN tunnels
Time Stamping
Cryptographic marking documents with Time Stamps in order to ensure the moment when a specific operation was performed
Advantages
The implementation of a Public Key Infrastructure and hardware protection in the Information Technology environment provides the foundation and the low-level elements for protecting your business. By using cryptography and digital certificates the business not only accomplishes compliance with international regulations/industrial standards (GDPR, PCI-DSS, SWIFT, ISO 27000, etc.) but enhances its security overnight.
The cryptography as a whole provides fundamental security services: Confidentiality, Integrity, Authenticity and Non-Repudiation.