What is Automated Bots Protection?
Automated Bots Protection (Advanced Bots Protection) offers comprehensive protection of web applications, mobile apps and APIs from automated threats like bots by providing precise bot management across all channels, combining behavioral modeling for granular intent analysis, collective bot intelligence and fingerprinting of browsers, devices and machines.
Challenges
Organizations rely on robotic process automation, essentially the use of bots, to be more efficient and boost productivity. Good bots, like those used to crawl websites for web indexing, content aggregation and market intelligence, free human resources to focus on other responsibilities. Of concern are the bad bots deployed by bad actors to disrupt network services, steal data, perform fraudulent activities and even spread fake news.
Bots have evolved significantly since their origins as simple scripting tools that used command-line interfaces. Bot developers now use JavaScript and HTML5 web technologies to enable bots to leverage full-fledged browsers. The bots are programmed to mimic human behavior when interacting with a website or app to move the mouse, tap and swipe on mobile devices and generally try to simulate real visitors in order to evade security systems.
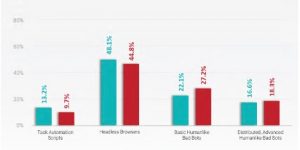
Classification of existing bots
At the moment we can divide bots into four types:
First Generation - Script Bots
- Typically use just one or two IP addresses to execute thousands of webpage visits to scrape content or spam forms.
- Easy to detect and blacklist thanks to repetitive attack patterns and a small number of originating IP addresses
Second Generation – Headless Browsers
- Leverage headless browsers — which are website development and testing tools — to tap their abilities to run JavaScript and maintain cookies
Third Generation – Single Interaction
- Mimic human behavior such as moving the mouse, scrolling and clicking links to navigate websites
- Exhibit sophisticated behaviors that may overcome certain challenges but cannot fool interaction-based detection, such as CAPTCHA or invisible challenges
Fourth Generation – Distributed, Mutating Bots
- Rotate through large numbers of user agents and device IDs — generating just a few hits from each to avoid detection
- Make random mouse movements (not just in a straight line like third-generation bots) and exhibit other humanlike browsing characteristics
- Record real user interactions, such as taps and swipes on hijacked or malware-laden mobile apps, to be able to replicate the movements and blend in with human traffic and circumvent security measures
How can this technology help you?
Modern Bot Protection solutions face a dual challenge: to identify attacker bots which are increasingly sophisticated at emulating human users and to distinguish malicious bots from legitimate bots, which can be very important for an organization’s day to day operations.
Currently, three main approaches are used to detect and manage bots:
Static approach
uses static analysis tools to identify header information and web requests known to correlate with bad bots. This technique is passive and can only detect known and active bots.
Challenge-based approach
uses active challenges or tests that are difficult or impossible for bots to perform to identify bots. Commonly used challenges include CAPTCHA verification, the ability to run JavaScript, of the acceptance of cookies.
Behavioural approach
evaluates the activity of potential users and matches that activity against known patterns to verify user identity. This technique uses several profiles to classify activity and distinguish between human users, good bots, and bad bots.
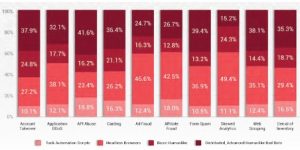
Advantages
The advantage of having a solution that is able to detect even the most sophisticated type of bots is that it allows an organization to protect their infrastructure against the most common type of automated bot attacks:
Account Takeover
Account takeover (ATO) is an attack in which criminals take unauthorized ownership of online accounts using stolen usernames and passwords
Carding
In carding attacks, criminals use bots to test lists of recently stolen credit or debit card information on merchant sites
Skewed Analytics
Skewed analytics are the result of activity and interaction data of your web traffic that are erroneous due to a high volume of non-human traffic.
Web Scraping
Web scraping is a process where bots crawl websites to continuously capture pricing data and product descriptions at scale.
Denial of Inventory
In denial of inventory attacks, bad actors use malicious hoarder bots to an item thousands of times to a shopping cart over the course of a few days until the item’s inventory is depleted