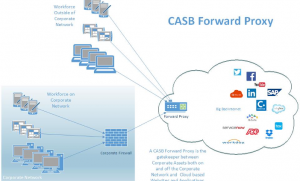
A cloud access security broker (CASB) is on-premises or cloud based software that sits between cloud service users and cloud applications, and monitors all activity and enforces security policies.
A CASB acts as a gatekeeper, allowing the organization to extend the reach of their security policies beyond their own infrastructure.
Challenges
CASBs are particularly useful in organizations with shadow IT operations or liberal security policies that allow operating units to procure and manage their own cloud resources.
The data that CASBs collect can be used for reasons other than security, such as monitoring cloud service usage for budgeting purposes.
Data security
Phenomena such as BYOD (bring your own device) policies, the growing popularity of SaaS and cloud apps, and the rise of Shadow IT make restricting cloud app access to a defined set of endpoints a difficult task.
BYOD, Shadow IT, and Increased Cloud Usage
It can be difficult to guard against the malicious intent or negligence of authorized users. To detect suspicious insider behavior, organizations need a comprehensive view of their normal usage patterns.
Regulation
As data moves to the cloud, organizations will want to ensure they are compliant with regional regulations that ensure data privacy and security.
How can this technology help you?
Restrict unauthorized access everywhere
A CASB solution is securing and monitoring access to information within the cloud, not just at the perimeter.
Identify account takeovers
Monitors for suspicious login and activity behavior 24/7. If a potential issue is detected, a CASB can automatically take action to revoke access from the suspected account.
Internal and external data access controls
Monitors behavior within cloud applications, not just access to it at the perimeter. Your information security team needs to be able to see what is going on within cloud applications, including: who is accessing what information, who is sending and sharing what type of information, what cloud apps are connected via OAuth, and more.
Advantages
A CASB can offer a variety of services such as monitoring user activity, warning administrators about potentially hazardous actions, enforcing security policy compliance, and automatically preventing malware.
Visibility
Discover shadow IT cloud services and gain visibility into user activity with sanctioned cloud applications.
Compliance
Identify sensitive data in the cloud and enforce DLP policies to meet data residency and compliance requirements.
Data Security
Enforce data-centric security such as encryption, tokenization, access control, and information rights management.
Threat protection
Detect and respond to negligent or malicious insider threats, privileged user threats, and compromised accounts.